Advanced Technology Devices

Advanced Technology Devices
Radiation Safety
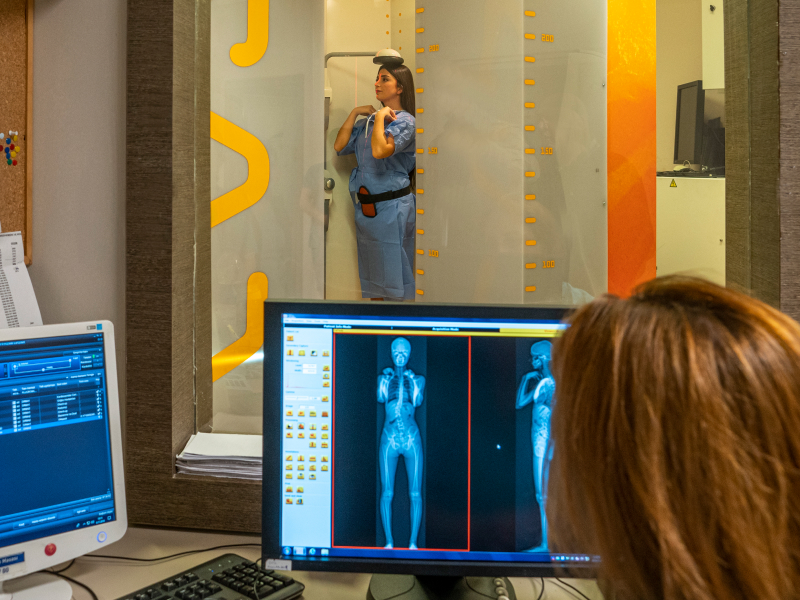
The EOS device significantly reduces radiation exposure, offering up to 85% less radiation compared to conventional methods. With the micro-dose protocol, this exposure can be further minimized, preventing radiation-related issues, especially in frequently taken images for spinal deformities. EOS allows simultaneous front and side imaging, providing 3D assessments of spinal deformities. This three-dimensional imaging from upright films is crucial for better understanding and planning treatments. The EOS system is available in approximately 300 centers worldwide.
For the analysis of posture and gait disorders, the Diers 4D Motion Lab surface scanning device and Diers Myoline devices for muscle strength evaluation are used. Based on the information from these devices, patient posture analyses are conducted, exercise programs are created, and follow-ups are performed. Thus, the use of radiation-emitting imaging devices is reduced in tracking analysis and treatment outcomes. With the Diers 4D Motion Lab and Diers Myoline devices, pre-surgery strengthening exercises are planned for adult patients undergoing spinal surgery, speeding up post-surgery recovery.
The Siemens Somatom Force CT scanner, with its ultra-low dose feature, can capture images of the entire spine at a lower dose than conventional film.
These technologies, which provide low-dose radiation and clearer, 3D imaging orthogonal to the anatomical axes, are used to prevent the side effects of frequent radiation exposure in spinal diseases like scoliosis and kyphosis that are often seen in children.
In Spinal Health, Siemens Magnetom 1.5T Avanto Fit and Siemens Magnetom 3T Skyra MRI devices are used for precise imaging in the diagnosis of spinal and spinal cord diseases. Magnetic resonance (MR) provides detailed imaging of soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments, discs, and nerves, assisting in treatment decisions.
Surgery Safety
In spinal surgeries requiring instrumentation like screw placement in children and adults, the Medtronic O-arm imaging device and the S7 Stealth Station real-time navigation device are used to ensure secure and precise placement of screws and other instruments.
The use of navigation in surgery increases the safety of implant and screw placement, preventing vascular and nerve injuries.
It helps avoid suboptimal screw placements, increasing screw stability, and reducing mechanical complications like screw loosening and revision surgery rates.
Surgeries are performed using the specially developed Allen Advanced Table for spinal surgery. Compared to traditional tables, it eases positioning of the patient’s body and spine, reduces abdominal pressure, minimizes bleeding, and increases surgical safety and efficiency.
It allows positioning of the legs during the procedure, facilitating spinal alignment and shape maintenance.
Different tables attached to the same table allow patients to be positioned supine and laterally, making it easy to shift patients from one position to another.
In surgeries, the specially developed Zeiss Tivato 700 surgical microscope is used for spinal surgeries. Karl Storz Ethicon Videothoracoscopy There are Karl Storz & Ethicon instruments for performing closed spinal surgeries with video-thoracoscopy. These devices enable minimally invasive surgeries, reducing surgical damage to muscles and other soft tissues.
Digital Surgery Preparation
Treatments are planned using the “Spine Surgery Planning and Simulation” software, which provides ideal planning of adult spinal diseases and prevention of mechanical complications, developed from scientific studies conducted within the European Spine Study Group (ESSG) and pioneered by us.
In the surgical treatment of spinal diseases, the method of stabilizing specific parts of the spine and fusing the vertebrae (fusion) is commonly applied. Since the vertebrae involved in the surgery are stabilized in a specific position with rods, the position of stabilization is crucial.
This positioning is determined based on the anatomical structure of the operated spinal area and varies from person to person, so rods are provided straight by medical companies. These rods are shaped by the surgeon during surgery. In the past, this shaping was done based on experience, feeling, and eye judgment, but today, advanced technologies such as computer programs and mobile applications are used.
The personalized treatment planning approach also reduces costs by preventing complications and repeat surgeries, providing significant gains in health planning and economy.
In our unit, the “risk calculation” device, a product of the European Spine Study Group (ESSG) that calculates post-surgery risks for adult spinal patients, is used. Planning surgery based on these risks reduces surgical complications.
Machine learning and deep learning, which detect interactions by examining data directly without any bias or clinical information and improve predictive ability as new patient data is added, are large data analysis methods used in the universal application of personalized analysis.
With the use of biostatistics and medical informatics methods, the limits and formulas of scoring systems are updated, and the analysis and planning methods are constantly evolving to adapt to the changing society, surgery methods, and materials, maintaining their up-to-date structure.
With the 3D printer used for the planning and safe surgery of complex spinal deformities, personalized spine models are produced precisely and used for anatomical identification before and during surgery.
It is also possible to perform surgeries on these models, allowing the surgeon to review all procedures mentally before starting the surgery.